Chronic inflammation: what is it and how to minimise it
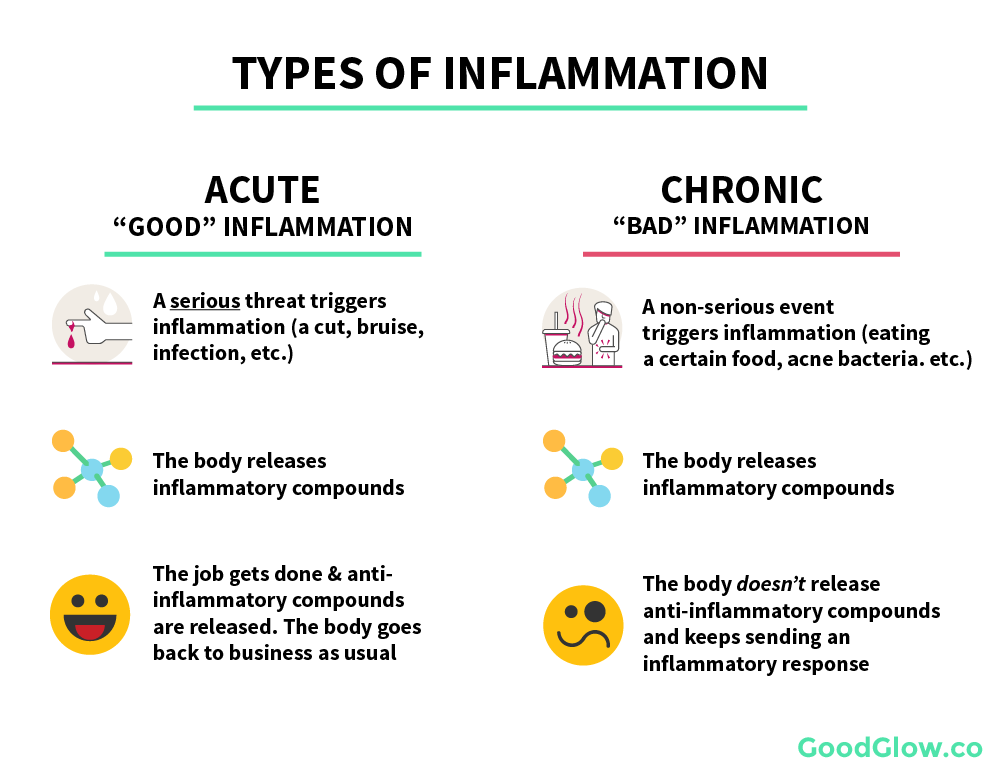
Acute inflammation is what the body requires to assist healing and this is a normal response. It is what you see at the site of a sprain/strain injury, sinusitis, a sore throat and sunburn.
Chronic inflammation is different, as it is not a normal response. It is due to viral or microbial infection or poor lifestyle choices (environmental factors). It is what you are doing to your body that is creating it. It is a low grade, often silent type of inflammation which is the big driver of nearly every disease, can sabotage your athletic performance,and may even result in muscle loss. It is abnormal inflammation which has an impact on your nervous system and spinal health. It does not benefit the body. It signals failure to eliminate the cause of the initial acute inflammation. Chronic inflammation can lead to asthma, Chron’s disease (Bowel), arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankyloses spondylitis and chronic back pain. Nerve cells, skeletal (bone) cells and cardiac (heart) cells are especially vulnerable to the effects of chronic inflammation. In some cases injuries and trauma to the body that are left untreated can lead to chronic inflammation.
5 top tips to reduce inflammation
- Foods to avoid
High saturated fats, trans fats and foods with a high glycemic index should be avoided along with vegetable fats, processed foods and grain fed beef. The average diet in modern society has 20 times more inflammatory fats compared to anti-inflammatory ones. Our Paleolithic ancestors ate about 50:50.
- Foods to include
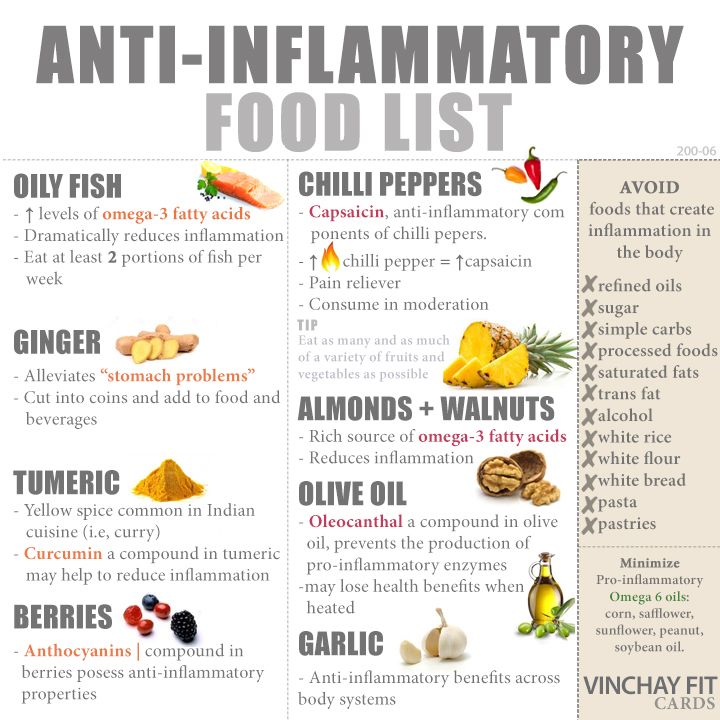
It is important to increase anti-inflammatory foods to offset the effects of inflammation.
Curcumin – Is one of the major compounds in turmeric and is a powerful anti-inflammatory. A safe daily maintenance dose is 10g per day. To boost the bioavailability of curcumin, adding piperine from black pepper increases it by 2000%!
Fish oil – Many studies support the benefit of fish oil in chronic inflammatory disease.
Vitamin C – Vitamin C in high doses is a great natural anti-inflammatory.
Bicarb soda – reduces the acid levels in the blood and moderates the immune systems inflammatory responses. Thus autoimmune problems, where the body is attacking itself may be eased. It helps the stomach to produce more acid to help digestion. Dissolve ½ a teaspoon (2g) in a cup of water.
- Exercise
Exercise keeps your body moving through its full range of movement and keeps your energy levels high. You are likely to heal faster and prevent chronic inflammation when you exercise on a regular basis.
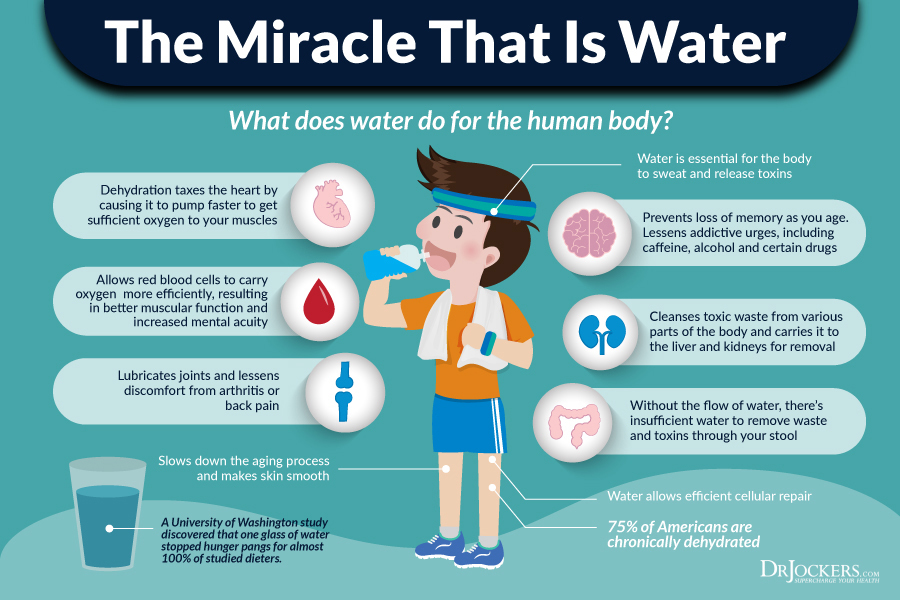
- Drinking water
There are many benefits from drinking adequate amounts of water that your body requires on a daily basis, apart from the obvious of keeping hydrated. The body requires water for proper function and it can reduce acidosis in the body and keep the body’s PH level in balance, which both in turn reduce chronic inflammation.
- Sleep
A study in 2006 concluded that sleep loss alters molecular processes that drive cellular immune activation and induce inflammatory cytokines, which in turn increase pain. Thus sleep deprivation can impact on inflammation and may even increase it!
Remember inflammation is not inherently bad – it’s actually part of the immune system that fights off viruses and bacteria and keeps you alive and well. It is the imbalance between acute and chronic inflammation that is detrimental to your health and repair from injury.
If you have any specific questions regarding your individual situation or you would love further information please contact us here at Global Chiropractic on 54443388 or email [email protected]
Global Chiropractic
SPECIAL OFFER: Global Chiropractic is currently offering new clients $180 worth of Chiropractic care for just $59. To get your $59 Chiropractic voucher, simply follow the link below: